Meat is an important source of protein for many people around the world, and global demand for meat is growing fast.
Over the past 50 years, meat production has more than tripled with up to 70 billion animals killed for meat every year.
According to the FAO, global meat consumption is projected to grow by 14% from 2020 levels and reach 374 million tons by 2030.
However, with up to 50% of global population growth expected to be in Africa, the continent’s meat consumption growth (at 30%) is the highest in the world, followed by the Asia and Pacific region (18%), Latin America (12%), North America (9%), and Europe (0.4%).
While Africa's population growth, demographics, and rapid urbanisation are some of the major drivers of meat consumption on the continent, there are several other factors that significantly influence the amount and type of meat consumed in any country or region.
These factors include economic growth, income levels, meat prices, tradition and cultural norms, religious beliefs, environmental interests, animal welfare issues, and ethical and health concerns.
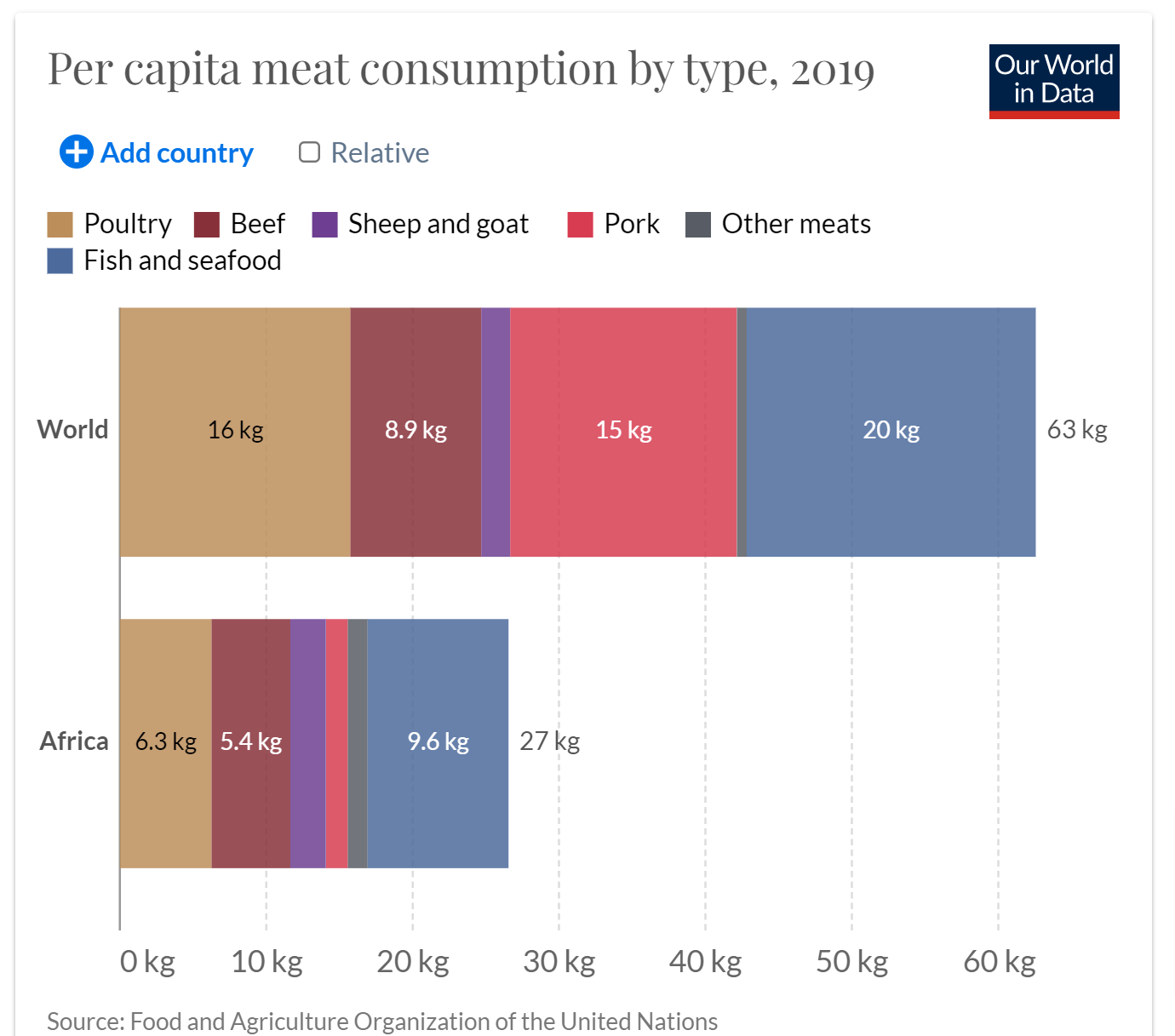
Across Africa, the graph below shows that, on a per-capita basis, people on the continent consume an average of 27 kilograms of meat, with fish being the most consumed (9.6kg), followed by poultry (6.3kg), beef (5.4kg), sheep and goat (2.4kg), and pork (1.5kg).